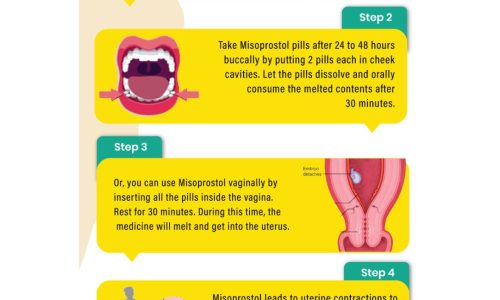
Macronutrients. It’s one of the latest words to hit the fitness and healthy eating scene, but what does it actually mean?
Macronutrients refer to the parts of food that we need to consume for energy. For us humans there are three broad classes of these – carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
It’s important to know in what quantities these should be consumed. As the recent Australian Government research suggests that major imbalances in macronutrients can increase the risk of chronic disease.
So what should we be eating and how much of it?
Proteins
Protein is a component of every cell in your body and is necessary in order to build and repair tissue.
So, if you’ve had a hard workout and want to help speed up your recovery. Then build lean muscle and maintain your healthy weight, then eating a high protein food is the way to go.
Reaching for some milk, fish, eggs or legumes should do the trick.
But the benefits are far more reaching than these things alone.
Long-term studies have shown that protein is beneficial for bone health, and lowers the risk of osteoporosis and fractures in old age.
Other studies have found that protein can boost metabolism and increase fat burning – good news to all of our ears.
According to The Australian Dietary Guidelines, the recommended daily percentage of energy in our diet from protein is between 15-25%.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates make up the most important part of our diet as they provide energy to cells such as the brain.
Much like a car needs fuel to run, your body needs carbohydrates to function. And so, it’s important to eat foods such as fruit, vegetables, breads, pasta, and dairy products.
From these, the body is able to produce glucose that’s a type of sugar that serves as your main energy source either immediately or later on.
The percentage of energy in our diet that should come from carbohydrates is between 45-65%.
Fats
Contrary to popular belief, not all fats are bad for us. In fact, we actually need certain ones to help us store energy, insulate us and protect our vital organs.
The fats we need are those that our bodies can’t produce itself, such as triglycerides and cholesterol, and come in the food form of unsaturated fats.
Good sources of monounsaturated fats are olive oil, avocados, and most nuts. Polyunsaturated fats can be found in sunflower oil and fish such as salmon and mackerel.
Numerous studies have shown that eating polyunsaturated fat can decrease the amount of bad cholesterol and raise the amount of good, whilst also lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease.
On the flipside, research from the Harvard School of Public Health found that even in small amounts, ‘bad’ trans fats could harm health. For every 2% of calories from trans fat consumed daily, the risk of heart disease rises by 23%.
The recommended daily percentage of energy in our diet from fats is 20-35%, with no more than 10% of this coming from saturated fat.
Remember
Whilst having a balanced diet is important, it’s also important to remember that everyone has individual nutrient requirements and these vary depending on factors such as age, weight and gender.
Daily intake recommendations are based on an average adult, however, your needs may be higher or lower.
Therefore, while it’s important to adapt this to your needs, it’s also imperative to consult a healthcare professional. Get advice before commencing on any health or wellness program.
Open Colleges made this infographic for you to learn more on eating the right ratio of macronutrients for our bodies. Check it out here: Opencolleges

![]()